The social structure in Sumer played a pivotal role in shaping one of the world's earliest civilizations. As the cradle of civilization, Sumer was characterized by a complex societal hierarchy that influenced various aspects of daily life, governance, and cultural development. Understanding this social structure allows us to appreciate the intricacies of Sumerian society and its lasting impact on future civilizations.
In this article, we will delve into the various components of Sumer's social structure, including its classes, roles, and responsibilities. By examining the relationships between different social groups, we can gain insights into how Sumerians lived, worked, and interacted with one another. The significance of social stratification in Sumer is not only an academic pursuit but also essential for comprehending the evolution of societal structures in human history.
Through a comprehensive exploration of Sumer's social hierarchy, we will highlight key figures, cultural practices, and the economic framework that defined this ancient society. Join us on this journey into the past as we uncover the layers of social organization that made Sumer a cornerstone of civilization.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Biographical Overview of Sumer
- The Social Classes of Sumer
- The Nobility and Ruling Class
- The Role of Priests in Sumerian Society
- Merchants and the Rise of Trade
- The Life of Laborers and Farmers
- The Role of Women in Sumer
- Conclusion
Biographical Overview of Sumer
Sumer, located in the southern part of Mesopotamia, is recognized as one of the first urban civilizations in the world, flourishing between 4500 BCE and 1900 BCE. The Sumerians are credited with numerous innovations, including the invention of writing (cuneiform), the wheel, and advances in mathematics and astronomy.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Southern Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) |
| Time Period | 4500 BCE - 1900 BCE |
| Major Cities | Ur, Uruk, Lagash, Nippur |
| Contributions | Cuneiform writing, the wheel, irrigation systems |
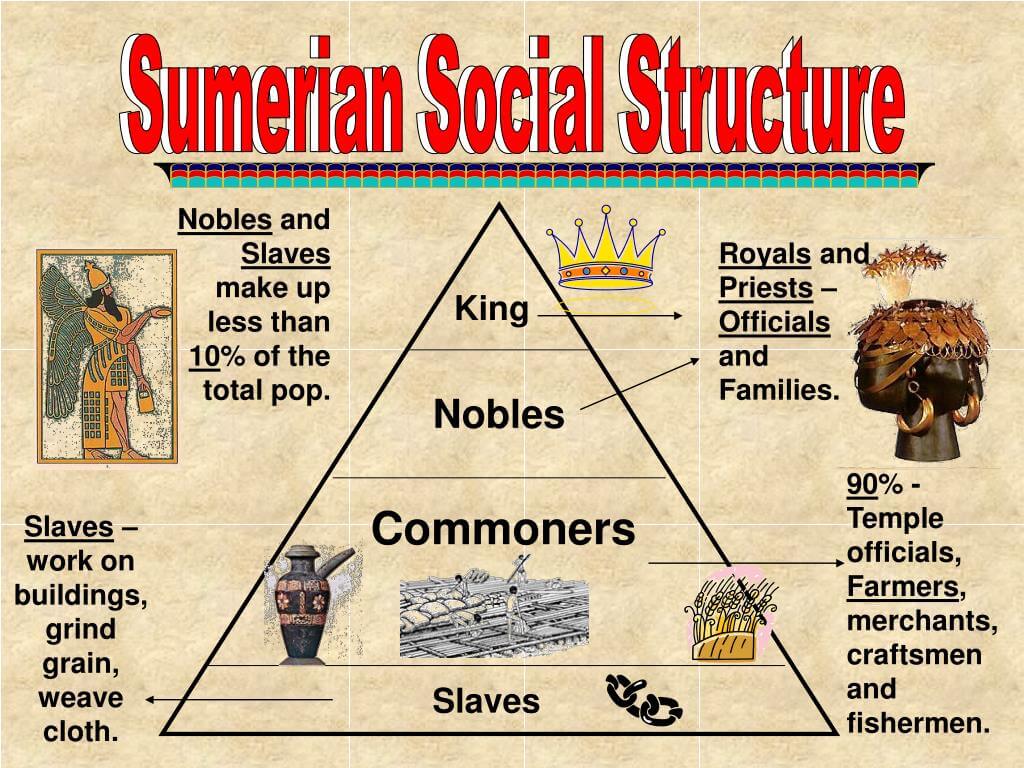
The Social Classes of Sumer
The social structure in Sumer was hierarchical and can be broadly divided into several classes. Each class played a specific role in the functioning of society, and the interactions between these classes were essential for maintaining social order.
- Nobility: This class included kings, government officials, and high priests who held significant power and wealth.
- Priests: Responsible for religious ceremonies and maintaining the temples, priests were influential figures in Sumerian society.
- Merchants and Artisans: This middle class was involved in trade, craftsmanship, and various skilled professions.
- Laborers and Farmers: The working class, consisting of farmers and laborers, formed the backbone of the economy.
- Slaves: At the bottom of the social hierarchy, slaves were often captured in war or born into servitude.
The Nobility and Ruling Class
The ruling class in Sumer consisted of kings and nobles who wielded extensive authority over their subjects. These rulers were often seen as divine figures, believed to be chosen by the gods to lead their people. As such, they held a crucial role in both governance and religion.
The nobility was responsible for enacting laws, collecting taxes, and overseeing major construction projects, such as temples and ziggurats. Their wealth was derived from land ownership and the labor of those beneath them in the social hierarchy.
The Role of Priests in Sumerian Society
Priests held a prominent position in Sumerian society, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people. They were responsible for conducting religious rituals, maintaining temple complexes, and ensuring that the favor of the gods was secured for the community.
Their influence extended beyond religious practices; priests often participated in civic duties, including advising rulers and managing economic resources. The temples they oversaw were not only places of worship but also centers of economic activity.
Merchants and the Rise of Trade
Merchants played a vital role in the economic landscape of Sumer. As trade expanded due to the development of cities and surplus agricultural production, merchants became essential in facilitating the exchange of goods both locally and internationally.
They established trade routes that connected Sumer with neighboring regions, allowing for the import of luxury items and the export of Sumerian goods. This burgeoning trade led to the rise of a wealthy merchant class, which contributed to the overall prosperity of Sumer.
The Life of Laborers and Farmers
Laborers and farmers constituted the largest segment of Sumerian society. They were responsible for agricultural production, which was the backbone of the economy. Their work included farming, irrigation, and the cultivation of crops such as barley and wheat.
The laborers often faced harsh conditions, working long hours under the supervision of landowners or nobles. Despite their hard work, they typically received a meager portion of the harvest, with much of the yield going to the ruling classes.
The Role of Women in Sumer
Women in Sumer had rights and responsibilities that varied depending on their social class. While the patriarchal structure dominated society, women could own property, engage in business, and even serve as priestesses.
In higher social classes, women might have enjoyed more privileges, including education and participation in religious ceremonies, while those in lower classes often worked alongside men in agricultural tasks.
Conclusion
The social structure in Sumer was intricate and multifaceted, characterized by distinct classes that contributed to the civilization's stability and growth. Understanding this hierarchy is crucial for appreciating the complexities of Sumerian life and its influential role in shaping future societies.
To further explore the fascinating world of Sumer, we encourage you to leave a comment, share this article, or continue reading more about ancient civilizations on our site. Your engagement helps us create more informative content for history enthusiasts!
Thank you for taking the time to delve into the rich history of Sumer with us. We hope to see you again soon for more insights into the wonders of ancient civilizations!
You Might Also Like
Step Brothers Costume: The Ultimate Guide To Dressing Like Will Ferrell And John C. ReillyIan Paice Young: The Journey Of A Legendary Drummer
Koi Fish History: A Journey Through Time
Paul Mescal And Pedro Pascal: A Deep Dive Into Their Connection
50 Most Marketable Athletes: A Comprehensive Guide
Article Recommendations
- Rottweiler Dachshund Mix
- Paul Wesley Liam Payne
- Johnny Somali Gets Punched
- Keely Shy
- Graham Nash Photo Of David Crosby
- The Marvelous Mrs Maisel Cast
- 2ct Solitaire Diamond Ring Price
- Antron Pippen
- Lamar Jackson Girlfriend
- News Rust