The social structure of Sumer was a complex tapestry woven from various layers of society, each with distinct roles and responsibilities. As one of the earliest known civilizations, Sumer flourished in Mesopotamia, now modern-day Iraq, and its societal organization was pivotal in shaping the dynamics of ancient life. This article delves into the intricacies of Sumerian society, exploring its hierarchy, roles, and the impact it had on subsequent cultures.
The Sumerians are credited with many firsts in human history, including the creation of writing, monumental architecture, and advanced urban planning. Their society was structured in a way that allowed for both specialization and collaboration, contributing to remarkable achievements in agriculture, trade, and governance. Understanding the social structure of Sumer provides valuable insights into the foundations of civilization and the evolution of societal norms.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will examine the various classes that comprised Sumerian society, the roles of men and women, the importance of religion, and the influence of Sumerian governance and economy. By the end of this article, readers will gain a thorough understanding of how the social structure of Sumer laid the groundwork for future civilizations.
Table of Contents
- Overview of Sumerian Society
- The Social Hierarchy of Sumer
- Roles and Responsibilities in Sumer
- Gender Roles in Sumerian Society
- Religion and Its Influence on Society
- Governance and Law in Sumer
- Economy and Trade in Sumer
- The Legacy of Sumerian Social Structure
Overview of Sumerian Society
Sumerian society emerged around 4500 BCE and is often considered one of the world's first civilizations. It was characterized by the development of city-states, each governed by a ruler or king. The Sumerians developed a unique culture with advances in writing, mathematics, and astronomy. Their society was heavily influenced by agriculture, with the fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers providing ample resources.
As Sumer grew, so did its population and complexity. The social structure of Sumer was hierarchical, with power concentrated at the top. This structure allowed for distinct roles, fostering specialization and collaboration among different classes. The Sumerians' achievements in architecture, literature, and administration were directly linked to this organized social framework.
The Social Hierarchy of Sumer
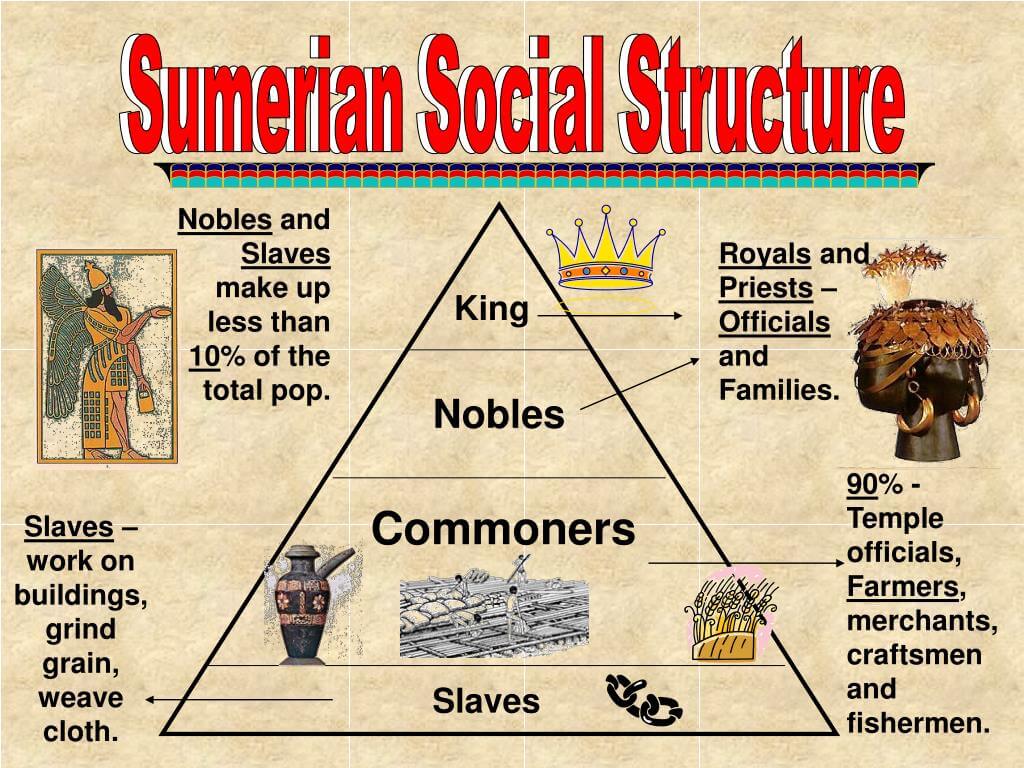
The social hierarchy in Sumer was divided into several distinct classes, each with its own roles and responsibilities. The major classes included:
- Nobility: This class comprised the ruling elite, including kings, priests, and high officials. They held significant power and wealth, often owning large plots of land.
- Priests: Priests played a crucial role in Sumerian society, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people. They conducted rituals and maintained the temples, which were central to Sumerian life.
- Merchants and Artisans: This class included traders and skilled craftsmen who contributed to the economy through their specialized skills and trade networks.
- Farmers and Laborers: The backbone of Sumerian society, farmers worked the land and provided food for the population. Laborers undertook various tasks, including construction and maintenance of infrastructure.
- Slaves: Slavery was prevalent in Sumer, with slaves often being prisoners of war or indebted individuals. They undertook menial labor and served the higher classes.
Diagram of Sumerian Social Structure
The following diagram illustrates the social hierarchy of Sumer:
- Nobility
- Priests
- Merchants and Artisans
- Farmers and Laborers
- Slaves
Roles and Responsibilities in Sumer
Each social class in Sumer had specific roles and responsibilities that contributed to the functioning of society. Let's delve into these roles:
Nobility and Governance
The nobility held power over the city-states and were responsible for making laws, collecting taxes, and maintaining order. They often led military campaigns and represented their city in diplomatic matters. Their authority was considered divinely sanctioned, further solidifying their position in society.
Priestly Duties
Priests were essential for performing religious ceremonies, maintaining temples, and interpreting the will of the gods. They managed vast temple estates, which were significant economic centers, and played a crucial role in the community's spiritual life.
Economy and Trade Responsibilities
Merchants and artisans were vital for economic growth. They engaged in trade, both within and outside Sumer, exchanging goods such as textiles, metals, and food. Artisans produced pottery, jewelry, and tools, showcasing Sumer's advanced craftsmanship.
Agricultural Contributions
Farmers and laborers formed the majority of the population. They cultivated crops like barley, wheat, and dates, and raised livestock. Their hard work ensured a stable food supply, which was crucial for the survival of the city-states.
Gender Roles in Sumerian Society
Gender roles in Sumer were distinct, with men typically occupying positions of power and women having limited rights. However, women in Sumer could own property, run businesses, and participate in religious practices. Notable female figures, such as priestesses, held significant influence, particularly in religious contexts.
Religion and Its Influence on Society
Religion was deeply embedded in Sumerian society, influencing all aspects of life. The Sumerians practiced polytheism, worshiping a pantheon of gods and goddesses who governed various aspects of nature and society. Temples were not only religious centers but also economic hubs, playing a crucial role in the community's livelihood.
Religious festivals and rituals were essential for maintaining social cohesion and expressing communal identity. The Sumerians believed that pleasing the gods ensured prosperity and protection for their city-states.
Governance and Law in Sumer
The governance of Sumer was characterized by city-states, each with its own ruler. These rulers were responsible for enforcing laws, collecting taxes, and maintaining public order. The Code of Ur-Nammu, one of the earliest known legal codes, exemplifies Sumerian legal principles, focusing on justice and protection for the vulnerable.
Rulers often claimed divine authority, which justified their power and decisions. This intertwining of religion and governance was a hallmark of Sumerian society, influencing future civilizations.
Economy and Trade in Sumer
The economy of Sumer was primarily based on agriculture, with trade playing a significant role in its growth. The Sumerians developed sophisticated irrigation systems that enhanced agricultural productivity. Surplus crops allowed for trade with neighboring regions, facilitating the exchange of goods and culture.
Trade networks extended beyond Mesopotamia, reaching as far as the Indus Valley and the Mediterranean. The Sumerians traded goods such as textiles, metalwork, and agricultural products, establishing themselves as a central hub of commerce in the ancient world.
The Legacy of Sumerian Social Structure
The social structure of Sumer has had a lasting impact on subsequent civilizations. Its hierarchical organization, religious practices, and governance models influenced the development of later societies in the region and beyond. The innovations in writing, law, and urban planning established by the Sumerians laid the groundwork for future advancements in human civilization.
Understanding the social structure of Sumer allows us to appreciate the complexities of early human societies and their contributions to the modern world. The lessons learned from Sumer continue to resonate in contemporary discussions about social organization and governance.
Conclusion
In summary, the social structure of Sumer was a multifaceted system that played a crucial role in the development of one of the world's earliest civilizations. Its hierarchical organization facilitated specialization and collaboration among different classes, leading to remarkable achievements in various fields. The influence of religion, governance, and trade shaped the social dynamics of Sumer and set the stage for future civilizations.
We encourage readers to engage with this topic further by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring related content on our site. Understanding the social structure of Sumer not only enriches
You Might Also Like
Brian Richards: The Rising Star In HollywoodFranchise In And Out: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Franchise Business Models
Delonte West: From NBA Star To Overcoming Life's Challenges
Jennifer Lien: A Comprehensive Look At The Life And Career Of The Talented Actress
Mister Zimi: The Rise Of A Fashion Icon
Article Recommendations
- Hallmark Mystery Schedule
- Johnny Somali Gets Punched
- Jakerman
- Rottweiler Dachshund Mix
- Sheryl Crow Liam Payne
- Sasha Calle Relationships
- Ukraine Military News Today
- Tyrrell Hatton
- P Diddy Costume Halloween
- The Price Is Right Milwaukee