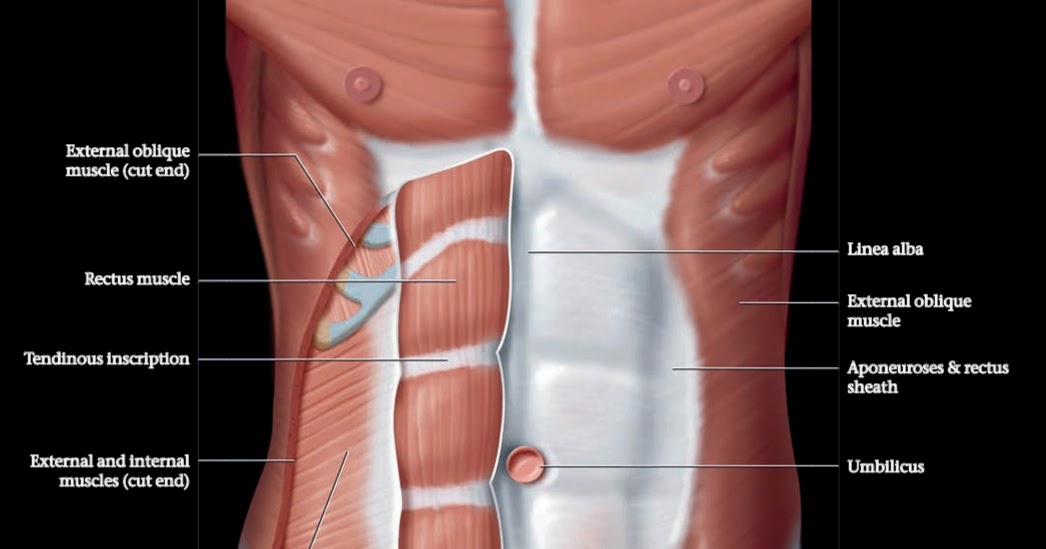
The human body is a marvel of intricate design, with every structure playing a vital role in maintaining functionality and efficiency. Among its many fascinating components is the tendinous inscription, a lesser-known but essential anatomical feature. Found within the rectus abdominis muscle, this fibrous band provides structural support and is pivotal in creating the well-known "six-pack" appearance seen in highly toned abdominal muscles. Beyond aesthetics, the tendinous inscription has important biomechanical roles that deserve closer attention.
Despite its relatively obscure name, the tendinous inscription is a cornerstone of core stability and strength. This unique structure is composed of connective tissue that divides the rectus abdominis into distinct sections, allowing for improved muscle control and function. It not only enhances the body's ability to flex and stabilize the spine but also serves as a key player in movements involving the trunk. Whether you're sitting, lifting, or twisting, the tendinous inscription works silently in the background to support these activities, making it a critical feature of musculoskeletal health.
In this article, we'll delve into the anatomy, functions, and clinical significance of the tendinous inscription. We'll explore its role in exercise performance, its contribution to overall posture, and its relevance in medical conditions such as hernias and muscle injuries. By the end, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of why this small but mighty structure is so vital. Stick around as we break down the science behind this fascinating component of the human body!
Table of Contents
- Anatomy and Location of the Tendinous Inscription
- Histological Composition and Structure
- Biomechanical Functions of the Tendinous Inscription
- Role in Core Stability and Spinal Support
- Impact on Physical Performance and Athletics
- Clinical Significance and Common Conditions
- Tendinous Inscription in Surgery and Medical Interventions
- Relation to Abdominal Hernias and Weakness
- Connections to Other Abdominal Muscles
- Exercises for Strengthening the Rectus Abdominis and Tendinous Inscription
- Common Injuries Involving the Tendinous Inscription
- Diagnostic Methods for Tendinous Inscription Issues
- Myths and Misconceptions About the Tendinous Inscription
- Importance in Posture and Everyday Movements
- Future Research and Advancements in Understanding
Anatomy and Location of the Tendinous Inscription
The tendinous inscription is a fibrous band that is anatomically located within the rectus abdominis muscle, which is a key component of the anterior abdominal wall. This muscle runs vertically from the pubic symphysis at the base of the pelvis to the xiphoid process and costal cartilage of the lower ribs. The tendinous inscription is responsible for dividing the rectus abdominis into smaller, segmented sections, which are often visible as the "six-pack" in individuals with low body fat percentages.
Each tendinous inscription is horizontally oriented and serves as an anchor point between the muscle fibers and surrounding connective tissues. Most individuals have three to four tendinous inscriptions in their rectus abdominis, although the exact number and placement can vary. These bands are strategically located to optimize the muscle's ability to contract effectively, particularly during activities that involve significant core engagement, such as lifting, twisting, and stabilizing the trunk.
The tendinous inscription is not just a cosmetic feature but an essential structural element. Its location within the rectus abdominis ensures that the muscle can function efficiently without overstretching or losing its mechanical advantage. This division into segments also allows for greater control and precision in muscle movements, which is particularly important for athletes and individuals who engage in demanding physical activities.
Additionally, the tendinous inscription plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the abdominal wall. By segmenting the rectus abdominis, it helps distribute forces more evenly across the muscle, reducing the risk of injury and strain. This feature is particularly beneficial during activities that place significant stress on the core, such as heavy lifting or rapid changes in direction. Understanding the anatomy and location of the tendinous inscription is crucial for appreciating its broader role in musculoskeletal health.
You Might Also Like
Essential Guide To Taraweeh Duas: Significance, Benefits, And PracticesChic And Timeless Ideas For A Girlie Room Makeover
Monaco Heuer: The Timeless Marvel Of The Watchmaking World
Mavado Bold: A Detailed Guide To The Iconic Timepiece
Innovative Condom Packaging: Design, Safety, And Sustainability
Article Recommendations
- Blondies Cookies Net Worth A Detailed Look At The Success Behind The Iconic Brand
- Top Muscular Actresses Fierce Fit Female Stars
- Expecting A Baby Ashantis Pregnancy Journey