Drawing isometric shapes can be a bit challenging, but with the right knowledge and practice, it becomes an engaging and rewarding experience. One of the most intriguing aspects of isometric drawing is creating an isometric circle, which is essentially an ellipse due to the nature of isometric projections. This type of drawing is crucial in technical fields such as architecture, engineering, and game design, where three-dimensional objects need to be represented on a two-dimensional plane. Understanding how to draw an isometric circle can enhance your technical drawing skills, making your designs more accurate and visually appealing.
At first glance, creating an isometric circle might seem complex, especially if you are new to isometric drawing techniques. However, with systematic guidance and practice, it becomes a straightforward task. This article aims to demystify the process, presenting a step-by-step approach that is easy to follow even for beginners. We will delve into the basics of isometric projection, explore the geometric principles behind isometric ellipses, and provide practical tips to help you master this crucial skill. By the end of the article, you'll have a solid understanding of how to draw an isometric circle and the confidence to apply this knowledge in your projects.
Whether you're a student, a professional, or an enthusiast looking to improve your drawing skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the necessary tools and techniques. We'll also address common questions and challenges that arise when drawing isometric circles and offer solutions to overcome them. So, prepare your drawing tools, and let's embark on this exciting journey to mastering the art of drawing isometric circles.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Isometric Projection
- Geometry of Isometric Circles
- Tools Required for Isometric Drawing
- Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing an Isometric Circle
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Practical Applications of Isometric Circles
- Enhancing Your Drawing Skills
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding Isometric Projection
Isometric projection is a method used in technical and engineering drawings to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane. It is a form of axonometric projection where the three axes appear at 120-degree angles to each other. This type of drawing preserves the dimensions along each axis, allowing for accurate representations without distortion. However, circles in isometric projection appear as ellipses due to the angles involved.
The principles of isometric drawing are grounded in geometry, specifically the use of equal scales along each axis. When creating isometric drawings, it is crucial to maintain consistency in the angles and dimensions to ensure that the representation remains accurate. This involves understanding how to manipulate your drawing tools to achieve the correct angles and scales, which is essential for creating an accurate isometric circle.
Isometric projection is widely used in various fields, including architecture, where it helps in visualizing complex structures, and in video game design, where it aids in creating immersive environments. Understanding the basics of isometric projection is the first step toward mastering the art of drawing isometric circles.
Geometry of Isometric Circles
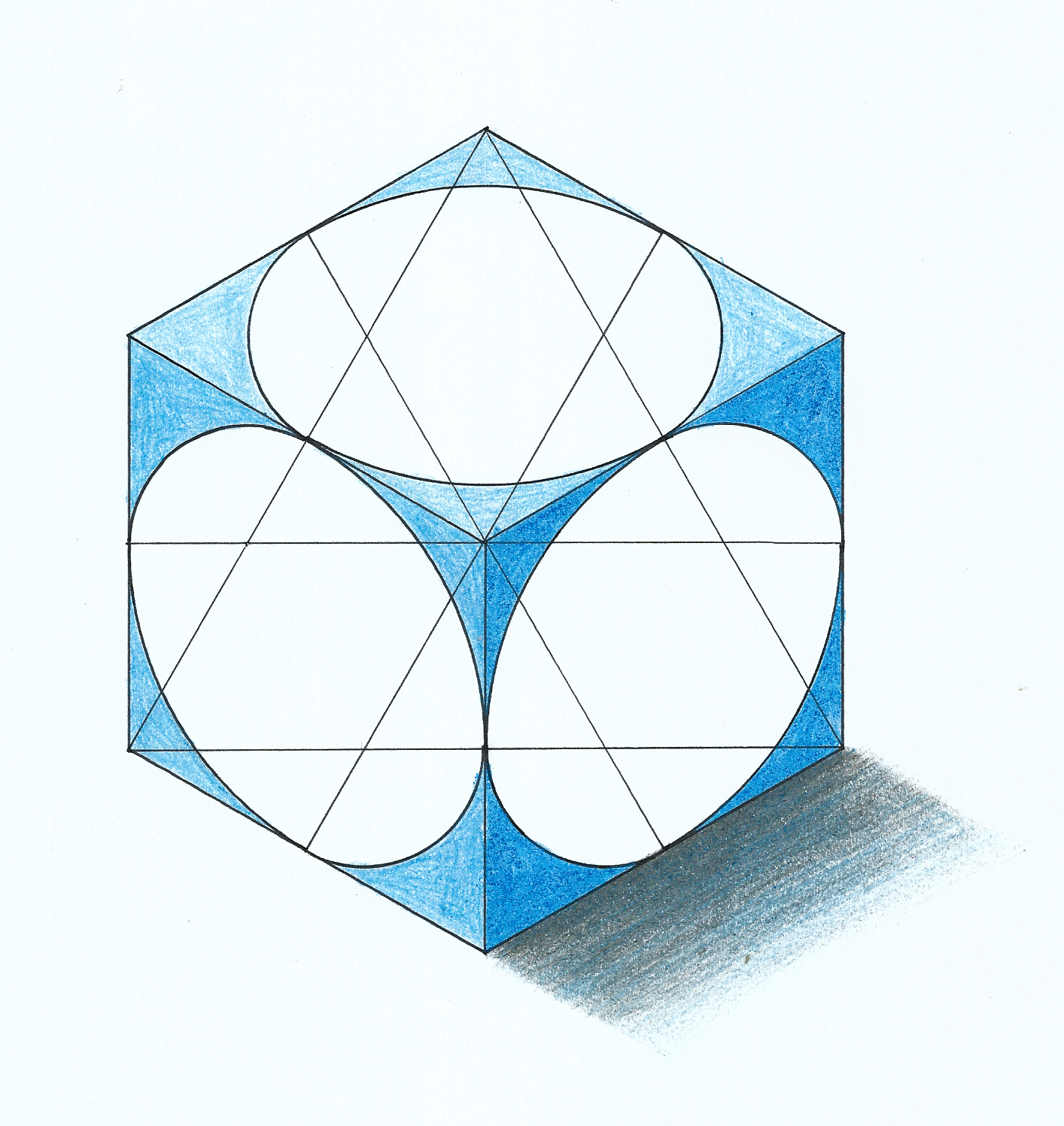
In an isometric drawing, a circle does not appear as a perfect circle but rather as an ellipse. This is due to the angles involved in isometric projection, where circles are viewed from an angle rather than head-on. The key to drawing an isometric circle lies in understanding the geometry of ellipses and how they are constructed.
The process involves plotting points along the circle's circumference and then connecting these points smoothly to form an ellipse. This requires accurate measurement and a steady hand to ensure the ellipse is symmetrical and correctly oriented within the isometric plane. Understanding the geometric properties of ellipses, such as the major and minor axes, is crucial in drawing an accurate isometric circle.
Geometrically, when drawing an isometric circle, you will work with the circle's diameter and use it to plot points within an isometric grid. These points are then used as references to draw the ellipse, ensuring it aligns correctly with the isometric axes. Mastering this technique requires practice and a good understanding of geometry, but once accomplished, it opens up a world of possibilities in isometric drawing.
Tools Required for Isometric Drawing
To draw an isometric circle, you'll need a few essential drawing tools that facilitate precision and accuracy. Here’s a list of recommended tools:
- Isometric Grid Paper: This specialized paper helps maintain consistent angles and scales, making it easier to draw isometric shapes and circles.
- Pencil: Use a medium-hard pencil (like an HB) for initial sketches and a softer pencil for final outlines.
- Eraser: A good quality eraser is essential for correcting mistakes and refining your drawing.
- Ruler: A clear plastic ruler helps in measuring and drawing straight lines accurately.
- Compass: Although not directly used for isometric circles, a compass helps in understanding circle properties and plotting points.
- Protractor: While isometric angles are set, a protractor can help in verifying angles if needed.
These tools, combined with practice and patience, will assist you in creating precise isometric circles. The key is to use these tools effectively, ensuring each step in the drawing process is executed accurately. Having the right tools not only enhances your drawing experience but also improves the quality of your finished work.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing an Isometric Circle
Drawing an isometric circle requires precision and an understanding of geometric principles. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you create an isometric circle:
- Prepare Your Workspace: Begin by setting up your workspace with the necessary tools mentioned earlier. Ensure your isometric grid paper is properly aligned on your drawing surface.
- Understand the Isometric Grid: Familiarize yourself with the isometric grid. The grid's triangular pattern will guide you in maintaining the correct angles while drawing.
- Plot the Circle’s Diameter: Determine the diameter of your circle. Use the grid to plot the endpoints of the diameter along one of the isometric axes.
- Find the Ellipse’s Axes: Use the plotted diameter to determine the major and minor axes of the ellipse. These axes will guide the shape and orientation of your ellipse.
- Plot Key Points: Using the axes, plot key points along the ellipse's perimeter. These points will serve as guides for drawing the curve.
- Connect the Points: Carefully connect the plotted points with smooth, curved lines to form the ellipse. This step requires precision and attention to detail to ensure symmetry.
- Refine the Ellipse: Use an eraser to clean up any unnecessary lines and refine the ellipse's outline. Ensure it appears smooth and symmetrical.
- Finalize Your Drawing: Once you're satisfied with the ellipse, go over it with a softer pencil or pen to finalize your drawing.
Practice is essential to perfecting your technique. With time and patience, you'll become proficient in drawing isometric circles, enhancing your overall isometric drawing skills.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When learning how to draw an isometric circle, beginners often encounter common mistakes that can affect the quality of their drawings. Here are some common pitfalls and tips on how to avoid them:
- Inaccurate Plotting: One of the most common mistakes is inaccurately plotting the points of the ellipse. This can lead to an uneven or distorted shape. To avoid this, always double-check your measurements and use the grid lines as guides.
- Uneven Ellipse: An uneven ellipse can result from incorrect proportions between the major and minor axes. Ensure you understand the geometry of an ellipse and maintain consistent scales along both axes.
- Overlapping Lines: Overlapping lines can make your drawing look messy. Use a light touch when sketching initial lines and erase any unnecessary marks before finalizing your drawing.
- Lack of Symmetry: Symmetry is crucial in isometric drawings. Use the grid to guide your drawing, ensuring symmetry in your ellipse.
- Rushing the Process: Drawing an isometric circle requires patience and attention to detail. Take your time with each step, and don't rush the process to ensure accuracy and quality.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can improve your technique and create cleaner, more accurate isometric drawings.
Practical Applications of Isometric Circles
Isometric circles have various practical applications across different fields. Understanding how to draw them can significantly enhance your capabilities in these areas. Here are some practical applications:
- Architecture and Engineering: In these fields, isometric drawings are used to represent complex structures and mechanical components. Isometric circles help accurately depict cylindrical objects, pipes, and round features.
- Game Design: Isometric views are popular in video game design, particularly in creating immersive environments. Isometric circles are used to create rounded elements and objects within these environments.
- Technical Illustration: Technical illustrators use isometric circles to represent rounded components and machinery parts in manuals and guides.
- Product Design: Product designers use isometric drawings to visualize and develop three-dimensional concepts, including circular features and elements.
The ability to draw accurate isometric circles is a valuable skill that can open up opportunities in various creative and technical fields. By mastering this technique, you can enhance the quality and precision of your work in these areas.
Enhancing Your Drawing Skills
Improving your drawing skills, especially in isometric projection, requires practice and dedication. Here are some tips to enhance your drawing skills:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to improvement. Dedicate time each day or week to practice drawing isometric shapes and circles.
- Study Geometry: Understanding the geometric principles behind isometric drawing will improve your ability to create accurate representations.
- Seek Feedback: Share your drawings with peers or mentors and seek constructive feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Experiment with Techniques: Explore different techniques and approaches to isometric drawing to find what works best for you.
- Learn from Others: Study the work of experienced artists and illustrators to gain insights into their techniques and styles.
Enhancing your drawing skills takes time and effort, but with persistence and a willingness to learn, you can significantly improve your abilities and produce high-quality isometric drawings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about how to draw an isometric circle and their answers:
What is the difference between an isometric circle and a regular circle?
An isometric circle appears as an ellipse due to the angles involved in isometric projection. Unlike a regular circle, which is viewed head-on, an isometric circle is viewed at an angle, resulting in an elliptical shape.
Why are isometric circles important in technical drawing?
Isometric circles are crucial in technical drawing as they provide a realistic representation of cylindrical objects and round features in three-dimensional space. They are essential in accurately depicting objects from multiple perspectives.
Can I use software to draw isometric circles?
Yes, various software programs like AutoCAD and Adobe Illustrator have tools for creating isometric drawings, including isometric circles. These programs offer precision and efficiency, making them popular choices in professional settings.
Is it necessary to use isometric grid paper?
While not necessary, isometric grid paper can significantly aid in maintaining consistent angles and proportions in your drawings. It serves as a guide, making it easier to create accurate isometric shapes and circles.
How can I improve my accuracy in drawing isometric circles?
Improving accuracy requires practice, understanding geometric principles, and using the right tools. Regular practice, careful measurement, and attention to detail will enhance your accuracy in drawing isometric circles.
What are some common challenges when drawing isometric circles?
Common challenges include maintaining symmetry, accurately plotting points, and avoiding overlapping lines. These challenges can be overcome with practice and attention to detail.
Conclusion
In conclusion, learning how to draw an isometric circle is an essential skill for anyone involved in technical drawing, design, or related fields. While it may seem complex at first, understanding the geometric principles and mastering the techniques involved can greatly enhance your drawing capabilities. This comprehensive guide has provided you with a detailed overview of the process, tools, and applications of isometric circles. With practice and dedication, you can achieve proficiency in this area, opening up opportunities for creativity and precision in your work.
Whether you're aiming to improve your technical drawing skills for professional purposes or personal interest, the knowledge gained from this guide will serve as a valuable foundation. Embrace the challenge, keep practicing, and continue to explore the fascinating world of isometric drawing. For further learning, consider exploring online resources, tutorials, and workshops to deepen your understanding and expand your skill set.
You Might Also Like
Unlocking Opportunities: Data Entry Remote Jobs Part-Time With No ExperienceThe Turbulent Priest: Unraveling The Legacy Of Thomas Becket
5 Signs A Man Is Broken: Understanding And Healing
How To Make Better Friends: A Comprehensive Guide To Building Meaningful Relationships
The Truth Behind The ASPCA: A Closer Look At The "Ripoff" Claims
Article Recommendations
- Sopa Vietnamita
- World Vision Pittsburgh Pa
- Halloween Lawn Decoration Chorus
- Adhd And Gaming
- Feline Mouth Cancer
- Mattress Removal
- Avatar Unalaq
- Tools For Twitch
- Jojo Siwa Real Name
- Toll Bridges In Washington State